설계/디자인 패턴
[디자인패턴] 생성 패턴 - 프로토타입 패턴
mint*
2025. 2. 17. 22:32
728x90
생성 - 프로토타입 패턴
프로토타입이란?
- 클래스에 의존하지 않고도 기존 객체를 복사할 수 있는 생성 디자인 패턴
프로토타입이 필요한 이유
- 객체의 정확한 사본을 만들고 싶다면, 먼저 새 객체를 생성하고 기존 객체의 모든 필드의 값을 새 객체로 복사해야한다.
- 만약 객체의 일부가 비공개이고, 외부에서 보이지 않아서 객체를 복사할 수 없다면?
- 또한 객체의 사본을 만들기 위해 기존 객체를 의존하는 것은 좋은 방법이 아니다.
- 만약 기존 객체가 인터페이스를 의존한다면, 정확한 동작을 알기 어려워 복사하기 어렵다.
프로토타입으로 문제 해결하기
프로토타입 패턴
객체를 복제할 때 new 키워드로 직접 생성하는 것이 아닌, 기존 객체를 복사하여 새로운 객체를 만들자
- 프로토타입은 새 객체가 복사할 객체에 의존하는 것이 아닌, 복사할 객체에 복사 프로세스를 위임한다.
- 복제 가능한 모든 객체들에 대한 공통 인터페이스를 선언한다.
- clone 메서드 구현 방법 : 객체를 생성하고, 객체의 모든 필드 값을 새 객체에게 전달한다.
- 복사할 객체가 복사 프로세스를 가지므로, private 필드도 접근이 가능하다.
clone을 지원하는 객체를 프로토타입이라고 한다.
-> 서브클래스의 대안이 될 수 있다.
구조
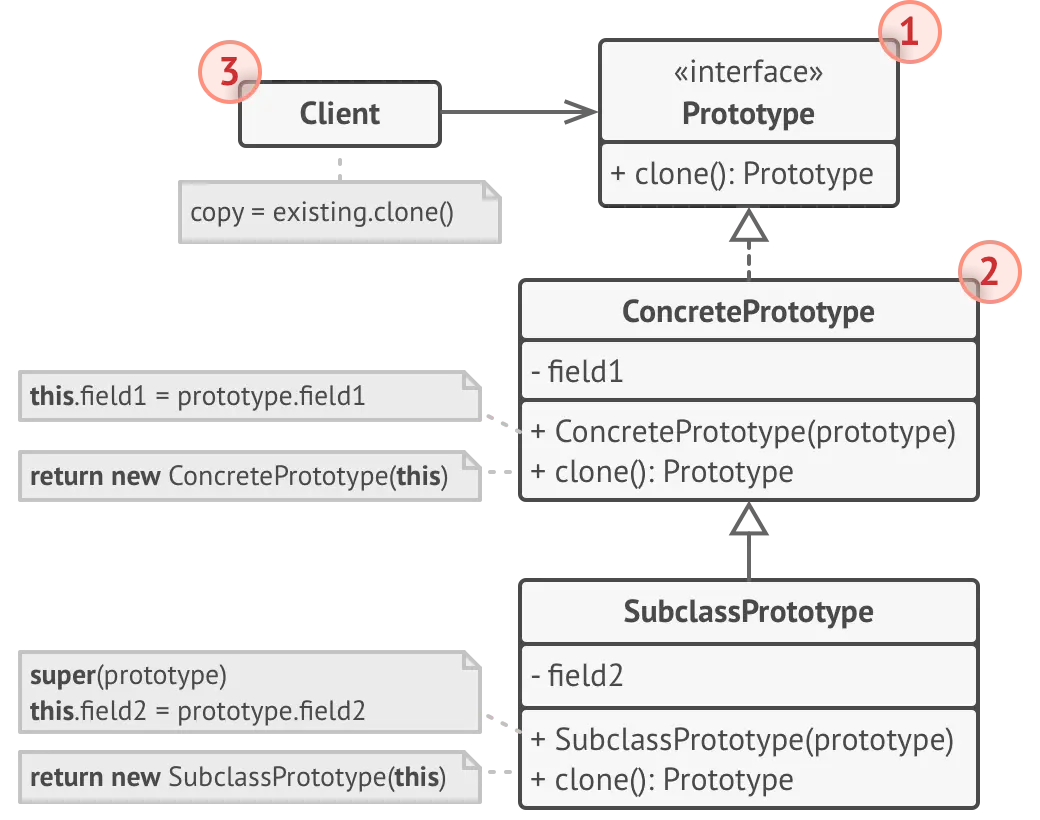
- 프로토타입 : 인터페이스, 복제 방법을 선언
- 구체 프로토타입 : 복제 방법을 구현한다.
- 클라이언트 : 프로토타입 인터페이스를 따르는 모든 객체의 사본을 생성할 수 있다.
interface Prototype {
Prototype clone(); // 복제 메서드 선언
}
class ConcretePrototype implements Prototype {
private String field1;
// 복사 생성자
public ConcretePrototype(ConcretePrototype prototype) {
this.field1 = prototype.field1;
}
@Override
public Prototype clone() {
return new ConcretePrototype(this); // 자신을 복제
}
}
class SubclassPrototype extends ConcretePrototype {
private String field2;
public SubclassPrototype(SubclassPrototype prototype) {
super(prototype);
this.field2 = prototype.field2;
}
@Override
public Prototype clone() {
return new SubclassPrototype(this);
}
}
class Client {
public void operation() {
ConcretePrototype existing = new ConcretePrototype();
Prototype copy = existing.clone();
}
}
프로토타입 레지스트리 구현
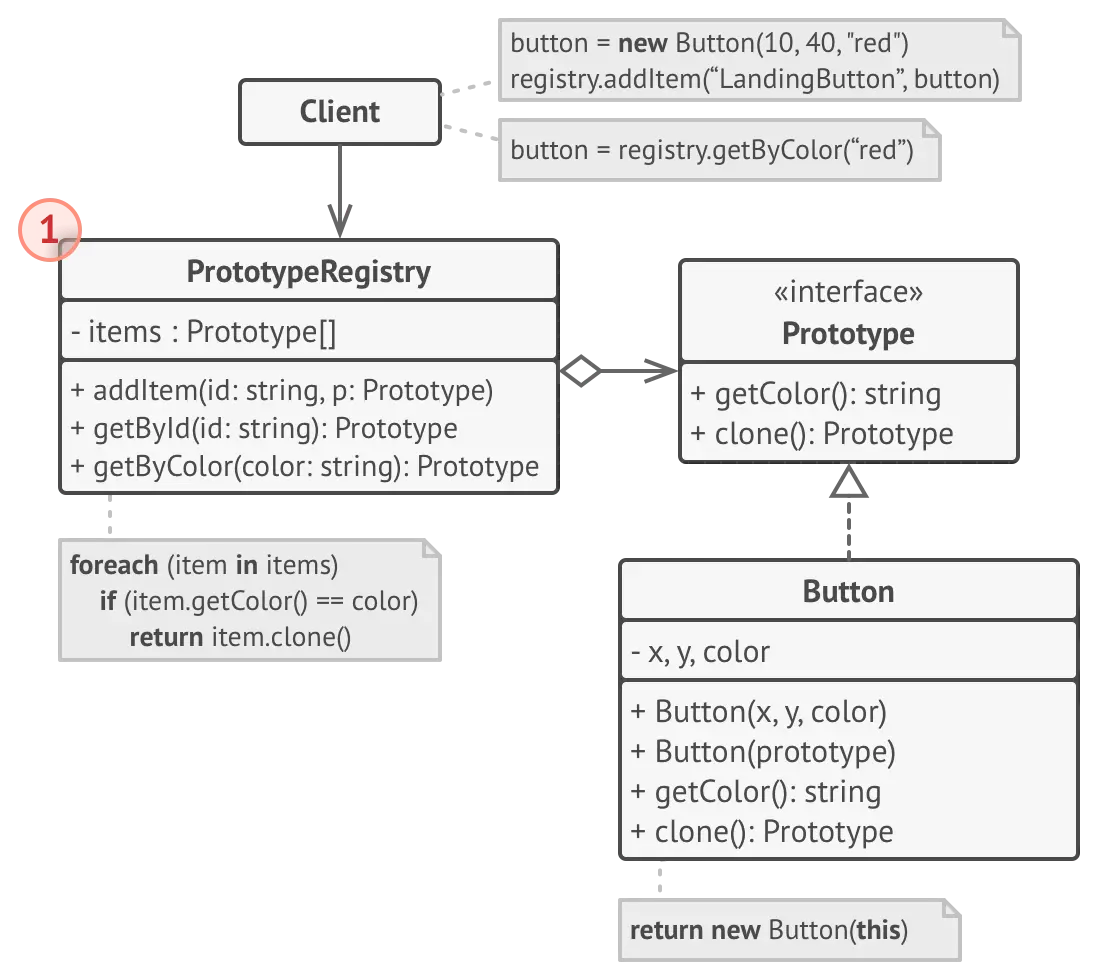
- 프로토타입 레지스트리 : 자주 사용하는 프로토타입들을 저장한다.
- 간단하게 이름-프로토타입 해시맵으로 저장할 수 있다.
예제 코드
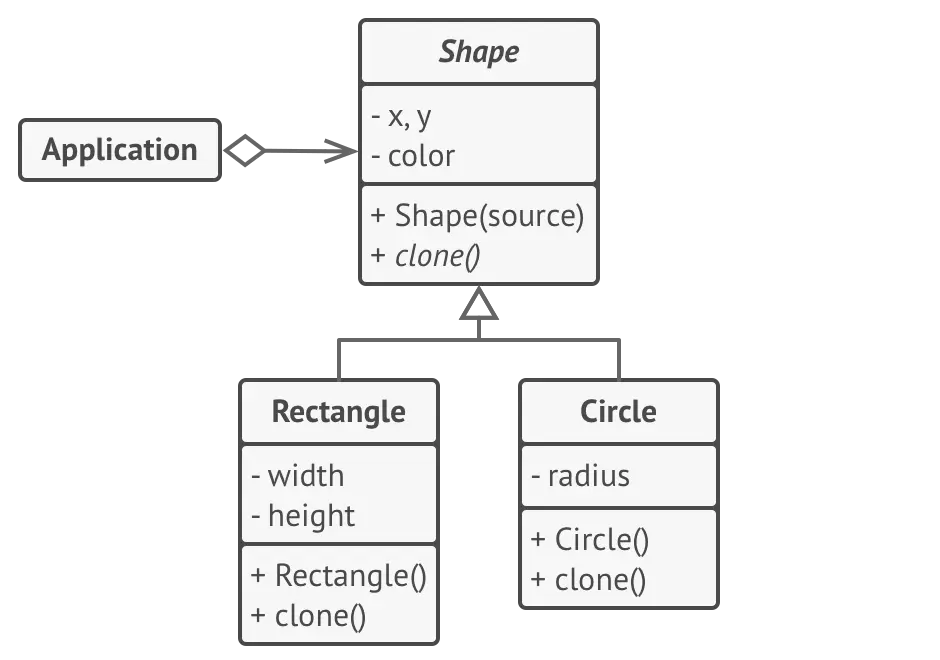
abstract class Shape {
private int x;
private int y;
private String color;
public Shape() {
}
public Shape(final Shape source) {
this();
this.x = source.x;
this.y = source.y;
this.color = source.color;
}
public abstract Shape clone();
public void setX(final int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(final int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setColor(final String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(final Rectangle source) {
super(source);
this.width = source.width;
this.height = source.height;
}
@Override
public Shape clone() {
return new Rectangle(this);
}
public void setWidth(final int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public void setHeight(final int height) {
this.height = height;
}
}public class Circle extends Shape {
private int radius;
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(final Circle source) {
super(source);
this.radius = source.radius;
}
@Override
public Shape clone() {
return new Circle(this);
}
public void setRadius(final int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
}public class Application {
private List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<>();
public Application(final List<Shape> shapes) {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setX(10);
circle.setY(10);
circle.setRadius(20);
shapes.add(circle);
Shape anotherCircle = circle.clone();
shapes.add(anotherCircle);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setWidth(10);
rectangle.setHeight(20);
shapes.add(rectangle);
}
public void businessLogic() {
List<Shape> shapesCopy = new ArrayList<>();
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
shapesCopy.add(shape.clone());
}
}
}
적용점
- 코드가 복사해야하는 구체 클래스에 의존하지 않아야할 때 사용 가능하다.
- 만약 인터페이스라면, 구체 클래스를 정확히 모르기 때문에 의존할 수 없다.
- 각 객체를 초기화하는 방식이 다른 서브 클래스 수를 줄이고 싶을 때 사용 가능하다.
- 만약 문서 형식마다 설정하는 방식이 다르다면 각각마다 새로운 클래스를 만들어야한다.
- 프로토타입을 사용하면, 미리 템플릿들을 저장하여 복제해서 사용할 수 있다.
class Document implements Cloneable {
private String content;
private String font;
private int fontSize;
public Document clone() {
return new Document(this); // 기존 객체를 복제해서 사용
}
}
// 클라이언트 코드
class DocumentManager {
private Map<String, Document> templates = new HashMap<>();
public DocumentManager() {
Document resume = new Document();
resume.setFont("Arial");
resume.setFontSize(12);
templates.put("resume", resume);
Document contract = new Document();
contract.setFont("Times New Roman");
contract.setFontSize(11);
templates.put("contract", contract);
Document report = new Document();
report.setFont("Calibri");
report.setFontSize(10);
templates.put("report", report);
}
public Document createDocument(String type) {
return templates.get(type).clone();
}
}
프로토타입은 비슷하지만 설정만 다른 객체를 만들 때, 매번 새로운 클래스를 만드는 대신 기존 객체를 복제해서 사용할 수 있다.
Reference
https://refactoring.guru/design-patterns/prototype
Prototype
/ Design Patterns / Creational Patterns Prototype Also known as: Clone Intent Prototype is a creational design pattern that lets you copy existing objects without making your code dependent on their classes. Problem Say you have an object, and you want to
refactoring.guru
728x90